Conifer:
Morphology, anatomy, and reproduction of Coniferales:
Coniferales (Pinus):
Gymnosperm: - Nonflowering, seed-producing plant. Pinus is commonly called conifers, because of the shape of the main body. The
main axis is elongated and the branches are elongated and the branches are
arranged in an acropetal manner (The lower branches are older and longer and the upper branches are shorter and younger). When these get covered with leaf, it
gives a typical cone-like shape to the plant. Thatswhy they called conifers.
Monoecious- Male and female reproductive, the structure is on
the same plant, i.e; monoecious.
Here we will be talking about branches, leaves because it is a spore-producing plant, and these spores i.e; microspore and megaspore, they are
producing on the leaves. So those leaves will be called the sporophylls.
Stem:
(b) Dwarf shoot
(I) Long shoot / long branch: There is a terminal bud, because of this, it continuously grows. That means this long the shoot is of unlimited growth because of terminal or optical bud.
(II) Dwarf shoot: In the case of the dwarf shoot there
is no such bud at the tip. They have limited growth.
When we draw the plant, we will
show the type of branches.
This long shoot is covered with scally
leaves, and from the axillary position of this leaves would arise the shorter shoot
or dwarf shoot.
If in the dwarf shoot, there
is no bud at the tip or it is going to have limited growth and as we have
written earlier these arrangements are acropetal which means the lower branches
are older and longer, and upper branches are younger and shorter. These branches arise from the axillary part of scally leaves. So, there are two types of
branches; long shoot and dwarf shoot.
Leaf:
(1)
Scally leaf’s: It covers the long shoot.
(2)
Foliar leaves: There are long needle-like leaves, these leaves are green and they are the ones which going to perform photosynthesis and
they arise at the tip of a short branch or the dwarf shoot. So, here foliar
leaves perform photosynthesis.
And the scally leaves which are going to
cover the body of the main trunk that function is protection.
(3) Sporophylls: They are actually going to produce spores or they have the spore-producing structures. So those leaves are known as sporophylls. Now, these sporophylls produce the microspores then we will call it microsporophyll and the other one will be called the macrosporophyll or megasporophyll.
The only thing is this
microsporophyll and megasporophyll, they are not found like this. They are
arranged around the central axis in a very compact manner spirally to make a
very compact structure which is called a cone or strobilus.
So, these leaves i.e; the
sporophylls they form the cone or strobilus. So, they can be a male and a
female cone. Microsporophylls would be forming a compact structure which will be
the male cone and the megasporophyll, they will form the female cone. The male
cones the arise in the cluster and they are smaller in size.
The female cones they
arise singly in the side of scally leaves. Normally because of the size, we may
find it like hanging structures.
The foliar or this
green needle leaves, they have sunken stomata, to minimize waterless. We see
this kind of stomata in conditions where water becomes a scares condition, like
plants are growing in dry areas.
In the case of Pinus, it grows in extremely cold conditions, so the water is available in the form of frozen i.e; either ice or snow. So, liquid water is not available in plenty of amounts. So, to minimize this waterless, they have sunken stomata, so their transpiration can be minimum.
The third type of leaves which are the sporophylls are not arranged in a free manner like everywhere in the plants. They are arranged compactly around the central axis to form of come or strobilus. The male cone is smaller in size but they grow in a cluster. Female cone which is larger in size they always grow singly in the scale leaves.
After mitotically unequal division it will produce –
Post pollination:
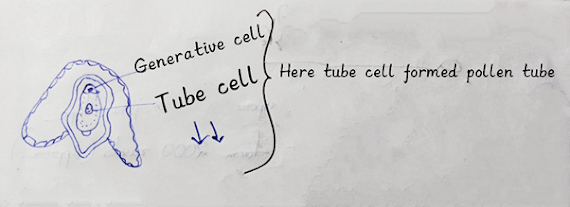
Post
pollination division occurs after the end of pollination. So, in pollen grain,
the exine ruptured which is present in the outside of the pollen grain, and the intine will form a pollen tube.
Intine
will form a pollen tube, after the ruptures of the exine.
At this time, the pollen tube will form tube cells. The generative cell will be divided into stalk cells and body cells. After, this the development
of the stalk cell will be stopped. Body cells will produce 2male gametes. (Non
motile).
Female Gametophyte
- Develop from only one megaspore - monosporic type.
- Functional megaspore - Free nuclear division - form 2000 nuclei (approx.)
- In the nuclei (wall formation happens) - from the periphery to central part - After wall formation, the cellular mass called an endospore.
(how?)
=> In endosperm 2 to 4 archegonial initial cell will form.
Transfer division-
(a) Primary neck cell
Fig: Development of female gametophyte
Pollination: Pollination will occur through air, for which microsporophylls will burst through the air, and too many and too many pollen grains will come out.
Pollination- Anemophillous type
Ovule secrets a Sugary substance and pollen grain comes through the air and attached to it. Female gametophyte sucks the pollen grain and then the microspore will go inside and will form a pollen tube. After pollination, the pollen grain will come towards the megasporophylls and will form a tube-like structure. The outer side of the pollen tube will rupture and will go inside through the neck and before that ventral cell degenerated. Also, there are 4 cells in the pollen grain-
(1) Stalk cell
(2) Two male gametes
(3) Tube cell
So, only one male gamete fuse with one female (egg) gamete and the other three (3) cell-
(a) Stalk cell
(b) Male gamete
(c) Tube cell
degenerated. After fusion-
Male gamete and female (egg) form zygote. The embryo will form after the zygote formation. After that seed will form from the embryo.
Fertilization:
Development of male and female gametophyte












Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box. ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon